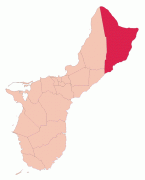
Yigo (Yigo Municipality)
The origin of the name "Yigo" is contested. Some state that it is derived from the Spanish word yugo, meaning "yoke". However, some sources refer to the area as Asyigo, meaning "the home of the person Yigo." Any record of such a person has been lost.
Before contact with Europeans, Yigo had a large number of villages. Latte stone structure remnants around Mount Santa Rosa and Mataguac indicate significant populations. During the Spanish-Chamorro Wars of the late seventeenth century, settlements in Yigo included Hanom, Tarague, Hinapsan, and Upi (now Northwest Field). Hanom, in particular, was a critical refuge because of its freshwater spring. The August 1679 defeat of the CHamorus at Hanom by a force of Spaniards and their allies from Nisihan led by José de Quiroga y Losada was one of the fiercest battles of the conflict. Following the subjugation of the CHamoru, the much reduced population was relocated to six villages centered on churches in the center and south of the island. Northern areas, including Yigo, were open to hunters and fishermen but not settlement.
In the early nineteenth century, wealthy residents of Hagåtña began purchasing fertile land in Yigo for agricultural uses. The area became known for producing cocoa beans, used to make hot chocolate for Hagåtña residents, as well as coffee, avocado, citrus, and copra. Upi was an important center of cattle ranching, while copra plantations were located along the northern coast, in particular. Following the Spanish–American War and beginning of the American administration, some CHamorus began to permanently settle in the north. The first elementary school in the area opened in 1912 and, in 1919, the U.S. administration authorized 25-year land use permits in Yigo. Our Lady of Lourdes Chapel was constructed in 1920; previously, Yigo residents journeyed to Hagåtña for mass. The first village store was started in 1925. However, by 1940, Yigo remained sparsely population with about 40 families.
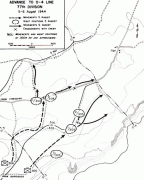
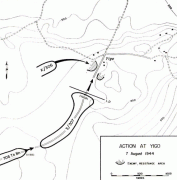
During the Japanese occupation of Guam from 1941 to 1944, some Hagåtña residents moved to Yigo to get away from the occupying Japanese force. The village was the site of a concentration camp during Japanese occupation of the island. The final battle between Japanese and American forces during the Battle of Guam occurred in Yigo on August 7 and 8, 1944, resulting in the destruction of the chapel and many homes. The South Pacific Memorial Peace Park was built by the Japanese Government and is dedicated to the many Japanese and American soldiers who died in the battle of Guam.
Following the war, the population of Yigo soared, first as it accommodated displaced persons from the south and then non-CHamorus who moved to Guam. The economy reoriented from agriculture towards the presence of Andersen Air Force Base and the population continued to grow with the construction of housing subdivisions throughout the village.
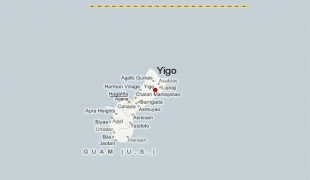
Map - Yigo (Yigo Municipality)
Map
Country - Guam
 |
 |
People born on Guam are American citizens but are politically disenfranchised, having no vote in the United States presidential elections while residing on Guam. Guam delegates to the United States House of Representatives have no vote on the floor. Indigenous Guamanians are the Chamoru, historically known as the Chamorro, who are related to the Austronesian peoples of Malay archipelago, the Philippines, Taiwan, and Polynesia. But unlike most of its neighbors, Chamorro language is not classified as a Micronesian or Polynesian language. Rather, like Palauan, it possibly constitutes an independent branch of the Malayo-Polynesian language family. As of 2022, Guam's population is 168,801. Chamorros are the largest ethnic group, but a minority on the multi-ethnic island. The territory spans 210 mi2 and has a population density of 775 /mi2. The Chamorro people settled the island approximately 3,500 years ago. Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan, while in the service of Spain, was the first European to visit the island on March 6, 1521. Guam was colonized by Spain in 1668. Between the 16th and 18th centuries, Guam was an important stopover for the Spanish Manila Galleons. During the Spanish–American War, the United States captured Guam on June 21, 1898. Under the 1898 Treaty of Paris, Spain ceded Guam to the U.S. effective April 11, 1899.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| USD | United States dollar | $ | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| CH | Chamorro language |
| EN | English language |