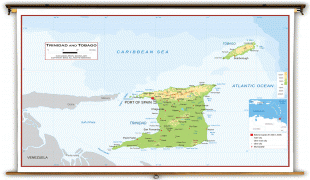
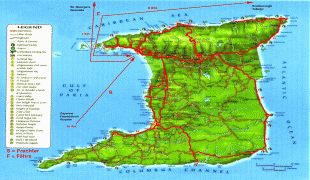
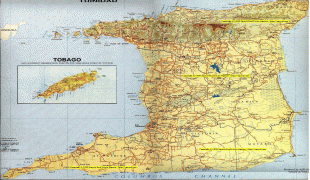
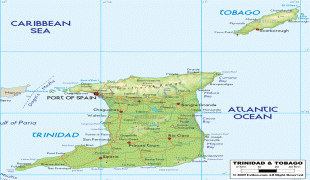
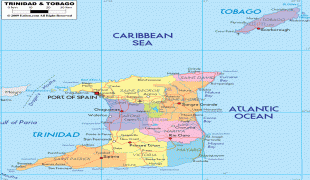
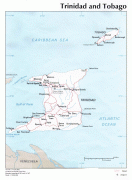
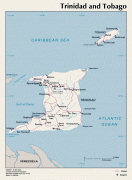
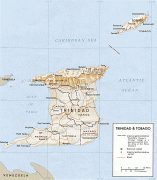
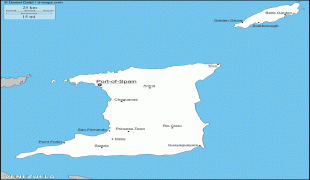
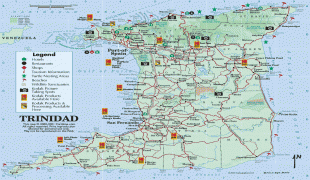
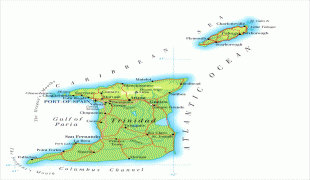
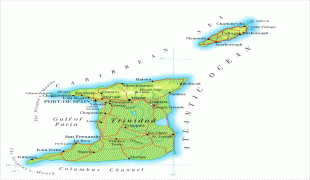
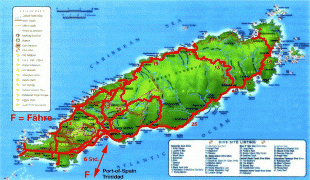
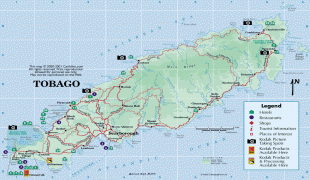
Trinidad and Tobago (Republic of Trinidad and Tobago)
 |
 |
| Flag of Trinidad and Tobago | |
The island of Trinidad was inhabited for centuries by Indigenous peoples before becoming a colony in the Spanish Empire, following the arrival of Christopher Columbus, in 1498. Spanish governor José María Chacón surrendered the island to a British fleet under the command of Sir Ralph Abercromby in 1797. Trinidad and Tobago were ceded to Britain in 1802 under the Treaty of Amiens as separate states and unified in 1889. Trinidad and Tobago obtained independence in 1962, becoming a republic in 1976.
Trinidad and Tobago has the 5th highest GDP per capita based on purchasing power parity (PPP) in the Americas for a sovereign state after the United States, Canada, The Bahamas and Guyana as of 2022. It is recognised by the World Bank as a high-income economy. Unlike most Caribbean nations and territories, which rely heavily on tourism, the economy is primarily industrial with an emphasis on petroleum and petrochemicals; much of the nation's wealth is derived from its large reserves of oil and natural gas.
Trinidad and Tobago is well known for its African and Indian cultures, reflected in its large and famous Carnival, Diwali, and Hosay celebrations, as well being the birthplace of steelpan, the limbo, and music styles such as calypso, soca, rapso, parang, chutney, and chutney soca.
Historian E. L. Joseph claimed that Trinidad's Indigenous name was Cairi or "Land of the Humming Bird", derived from the Arawak name for hummingbird, ierèttê or yerettê. However, other authors dispute this etymology with some claiming that cairi does not mean hummingbird (tukusi or tucuchi being suggested as the correct word) and some claiming that kairi, or iere, simply means island. Christopher Columbus renamed it "La Isla de la Trinidad" ("The Island of the Trinity"), fulfilling a vow made before setting out on his third voyage of exploration. Tobago's cigar-like shape, or the use of tobacco by the native people, may have given it its Spanish name (cabaco, tavaco, tobacco) and possibly some of its other Indigenous names, such as Aloubaéra (black conch) and Urupaina (big snail), although the English pronunciation is.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| TTD | Trinidad and Tobago dollar | $ | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| ZH | Chinese language |
| EN | English language |
| FR | French language |
| ES | Spanish language |