Uganda (Republic of Uganda)
 |
|
| Flag of Uganda | |
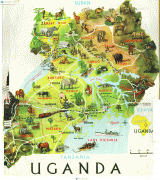
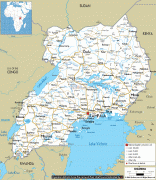
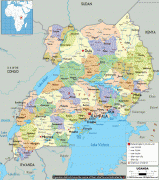
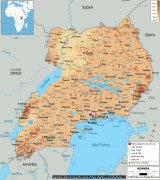
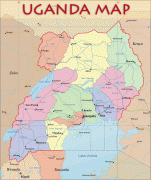
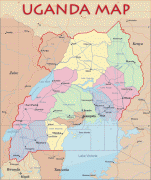
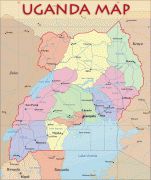
Uganda is named after the Buganda kingdom, which encompasses a large portion of the south of the country, including the capital Kampala and whose language Luganda is widely spoken throughout the country. From 1894, the area was ruled as a protectorate by the United Kingdom, which established administrative law across the territory. Uganda gained independence from the UK on 9 October 1962. The period since then has been marked by violent conflicts, including an eight-year-long military dictatorship led by Idi Amin.
The official language is English, although the Constitution states that "any other language may be used as a medium of instruction in schools or other educational institutions or for legislative, administrative, or judicial purposes as may be prescribed by law." Luganda, a central region-based language, is widely spoken across the Central and South Eastern regions of the country, and several other languages are also spoken including Ateso, Lango, Acholi, Runyoro, Runyankole, Rukiga, Luo, Rutooro, Samia, Jopadhola, and Lusoga. In 2005 Swahili, which is foreign and so viewed as being neutral, was proposed as Uganda's second official language, but this has yet to be ratified by parliament. In 2022 Uganda decided to make Swahili a mandatory subject in the school curriculum.
Uganda's current president is Yoweri Kaguta Museveni, who took power in January 1986 after a protracted six-year guerrilla war. Following constitutional amendments that removed term limits for the president, he was able to stand and was elected president in the 2011, 2016 and 2021 general elections.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| UGX | Ugandan shilling | Sh | 0 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| AR | Arabic language |
| EN | English language |
| LG | Ganda language |
| SW | Swahili language |