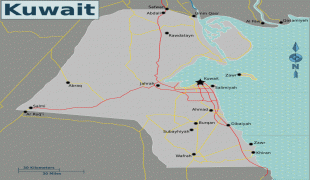
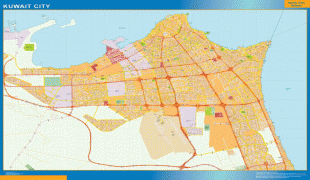
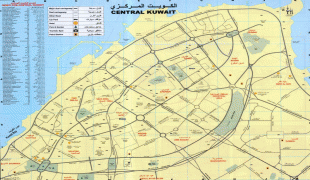
Kuwait City (Kuwait City)
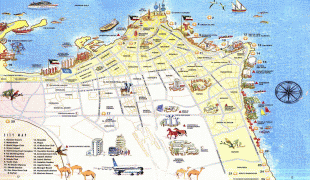
Kuwait City (مدينة الكويت) is the capital and largest city of Kuwait. Located at the heart of the country on the south shore of Kuwait Bay on the Persian Gulf, it is the political, cultural and economical centre of the emirate, containing Kuwait's Seif Palace, government offices, and the headquarters of most Kuwaiti corporations and banks. It is one of the hottest cities in summer on earth, with average summer high temperatures over 45 °C (113 °F) for three months of the year.
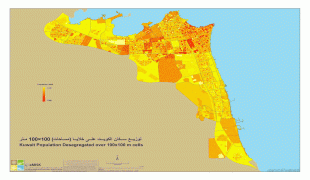
As of 2018, the metropolitan area had roughly 3 million inhabitants (more than 70% of the country's population). The city itself has no administrative status. All six governorates of the country comprise parts of the urban agglomeration, which is subdived in numerous areas. In a more narrow sense, Kuwait City can also refer only to the town's historic core, which nowadays is part of the Capital Governorate and seamlessly merges with the adjacent urban areas.
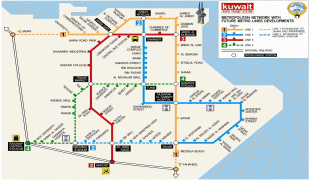
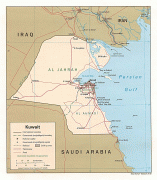
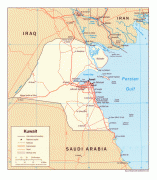
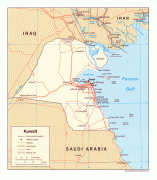
Kuwait City's trade and transportation needs are served by Kuwait International Airport, Mina Al-Shuwaik (Shuwaik Port) and Mina Al Ahmadi (Ahmadi Port).
In 1613, the town of Kuwait was founded in modern-day Kuwait City as a fishing village inhabited by fishermen. In 1716, the Bani Utubs settled in Kuwait. At the time of the arrival of the Utubs, Kuwait was still inhabited by a few fishermen and primarily functioned as a fishing village. In the eighteenth century, Kuwait prospered and rapidly became the principal commercial center for the transit of goods between India, Muscat, Baghdad and Arabia. By the mid 1700s, Kuwait had already established itself as the major trading route from the Persian Gulf to Aleppo.
During the Persian siege of Basra in 1775–1779, Iraqi merchants took refuge in Kuwait and were partly instrumental in the expansion of Kuwait's boat-building and trading activities. As a result, Kuwait's maritime commerce boomed. Between the years 1775 and 1779, the Indian trade routes with Baghdad, Aleppo, Smyrna and Constantinople were diverted to Kuwait. The East India Company was diverted to Kuwait in 1792. The East India Company secured the sea routes between Kuwait, India and the east coasts of Africa. After the Persian withdrawal from Basra in 1779, Kuwait continued to attract trade away from Basra.
Kuwait was the center of boat building in the Persian Gulf region. During the late eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, ship vessels made in Kuwait carried the bulk of trade between the ports of India, East Africa and the Red Sea. Kuwaiti ship vessels were renowned throughout the Indian Ocean. Regional geopolitical turbulence helped foster economic prosperity in Kuwait in the second half of the 18th century. Kuwait became prosperous due to Basra's instability in the late 18th century. In the late 18th century, Kuwait partly functioned as a haven for Basra's merchants fleeing Ottoman government persecution. According to Palgrave, Kuwaitis developed a reputation as the best sailors in the Persian Gulf.
During the reign of Mubarak Al-Sabah, Kuwait was dubbed the "Marseilles of the Gulf" because its economic vitality attracted a large variety of people. In the first decades of the twentieth century, Kuwait had a well-established elite: wealthy trading families who were linked by marriage and shared economic interests.
In 1937, Freya Stark wrote about the extent of poverty in Kuwait at the time:"Poverty has settled in Kuwait more heavily since my last visit five years ago, both by sea, where the pearl trade continues to decline, and by land, where the blockade established by Saudi Arabia now harms the merchants." Some prominent merchant families left Kuwait in the early 1930s due to the prevalence of economic hardship. At the time of the discovery of oil in 1937, most of Kuwait's inhabitants were impoverished.
From 1946 to 1982, Kuwait experienced a period of prosperity driven by oil and its liberal atmosphere. In popular discourse, the years between 1946 and 1982 are referred to as the "Golden Era". In 1950, a major public-work programme began to enable Kuwaitis to enjoy a modern standard of living. By 1952, the country became the largest oil exporter in the Persian Gulf region. In the following year, the country's annual oil income grew to $169 million. This massive growth attracted many foreign workers, especially from Palestine, Egypt and India and helped finance the development of a new master plan, which the state approved in 1952. In June 1961, Kuwait became independent with the end of the British protectorate and the sheikh Abdullah Al-Salim Al-Sabah became an Emir. Under the terms of the newly drafted constitution, Kuwait held its first parliamentary elections in 1963. Kuwait was the first Persian Gulf country to establish a constitution and parliament.
In the 1960s and 1970s, Kuwait was the most developed country in the region. Kuwait was the pioneer in the Middle East in diversifying its earnings away from oil exports. The Kuwait Investment Authority is the world's first sovereign wealth fund. From the 1970s onward, Kuwait scored highest of all Arab countries on the Human Development Index. Kuwait University was established in 1966. Kuwait's theatre industry was well-known throughout the Arab world. In the 1960s and 1970s, Kuwait's press was described as one of the freest in the world. Kuwait was the pioneer in the literary renaissance in the Arab region. In 1958, Al Arabi magazine was first published, the magazine went on to become the most popular magazine in the Arab world. Many Arab writers moved to Kuwait for freedom of expression because Kuwait had greater freedom of expression than elsewhere in the Arab world. Kuwait was a haven for writers and journalists from all parts of the Middle East. The Iraqi poet Ahmed Matar left Iraq in the 1970s to take refuge in the more liberal environment of Kuwait.
As of 2018, the metropolitan area had roughly 3 million inhabitants (more than 70% of the country's population). The city itself has no administrative status. All six governorates of the country comprise parts of the urban agglomeration, which is subdived in numerous areas. In a more narrow sense, Kuwait City can also refer only to the town's historic core, which nowadays is part of the Capital Governorate and seamlessly merges with the adjacent urban areas.
Kuwait City's trade and transportation needs are served by Kuwait International Airport, Mina Al-Shuwaik (Shuwaik Port) and Mina Al Ahmadi (Ahmadi Port).
In 1613, the town of Kuwait was founded in modern-day Kuwait City as a fishing village inhabited by fishermen. In 1716, the Bani Utubs settled in Kuwait. At the time of the arrival of the Utubs, Kuwait was still inhabited by a few fishermen and primarily functioned as a fishing village. In the eighteenth century, Kuwait prospered and rapidly became the principal commercial center for the transit of goods between India, Muscat, Baghdad and Arabia. By the mid 1700s, Kuwait had already established itself as the major trading route from the Persian Gulf to Aleppo.
During the Persian siege of Basra in 1775–1779, Iraqi merchants took refuge in Kuwait and were partly instrumental in the expansion of Kuwait's boat-building and trading activities. As a result, Kuwait's maritime commerce boomed. Between the years 1775 and 1779, the Indian trade routes with Baghdad, Aleppo, Smyrna and Constantinople were diverted to Kuwait. The East India Company was diverted to Kuwait in 1792. The East India Company secured the sea routes between Kuwait, India and the east coasts of Africa. After the Persian withdrawal from Basra in 1779, Kuwait continued to attract trade away from Basra.
Kuwait was the center of boat building in the Persian Gulf region. During the late eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, ship vessels made in Kuwait carried the bulk of trade between the ports of India, East Africa and the Red Sea. Kuwaiti ship vessels were renowned throughout the Indian Ocean. Regional geopolitical turbulence helped foster economic prosperity in Kuwait in the second half of the 18th century. Kuwait became prosperous due to Basra's instability in the late 18th century. In the late 18th century, Kuwait partly functioned as a haven for Basra's merchants fleeing Ottoman government persecution. According to Palgrave, Kuwaitis developed a reputation as the best sailors in the Persian Gulf.
During the reign of Mubarak Al-Sabah, Kuwait was dubbed the "Marseilles of the Gulf" because its economic vitality attracted a large variety of people. In the first decades of the twentieth century, Kuwait had a well-established elite: wealthy trading families who were linked by marriage and shared economic interests.
In 1937, Freya Stark wrote about the extent of poverty in Kuwait at the time:"Poverty has settled in Kuwait more heavily since my last visit five years ago, both by sea, where the pearl trade continues to decline, and by land, where the blockade established by Saudi Arabia now harms the merchants." Some prominent merchant families left Kuwait in the early 1930s due to the prevalence of economic hardship. At the time of the discovery of oil in 1937, most of Kuwait's inhabitants were impoverished.
From 1946 to 1982, Kuwait experienced a period of prosperity driven by oil and its liberal atmosphere. In popular discourse, the years between 1946 and 1982 are referred to as the "Golden Era". In 1950, a major public-work programme began to enable Kuwaitis to enjoy a modern standard of living. By 1952, the country became the largest oil exporter in the Persian Gulf region. In the following year, the country's annual oil income grew to $169 million. This massive growth attracted many foreign workers, especially from Palestine, Egypt and India and helped finance the development of a new master plan, which the state approved in 1952. In June 1961, Kuwait became independent with the end of the British protectorate and the sheikh Abdullah Al-Salim Al-Sabah became an Emir. Under the terms of the newly drafted constitution, Kuwait held its first parliamentary elections in 1963. Kuwait was the first Persian Gulf country to establish a constitution and parliament.
In the 1960s and 1970s, Kuwait was the most developed country in the region. Kuwait was the pioneer in the Middle East in diversifying its earnings away from oil exports. The Kuwait Investment Authority is the world's first sovereign wealth fund. From the 1970s onward, Kuwait scored highest of all Arab countries on the Human Development Index. Kuwait University was established in 1966. Kuwait's theatre industry was well-known throughout the Arab world. In the 1960s and 1970s, Kuwait's press was described as one of the freest in the world. Kuwait was the pioneer in the literary renaissance in the Arab region. In 1958, Al Arabi magazine was first published, the magazine went on to become the most popular magazine in the Arab world. Many Arab writers moved to Kuwait for freedom of expression because Kuwait had greater freedom of expression than elsewhere in the Arab world. Kuwait was a haven for writers and journalists from all parts of the Middle East. The Iraqi poet Ahmed Matar left Iraq in the 1970s to take refuge in the more liberal environment of Kuwait.
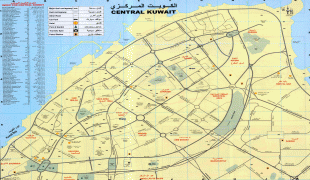
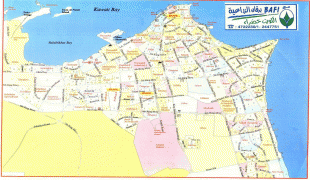
Map - Kuwait City (Kuwait City)
Map
Country - Kuwait
 |
 |
| Flag of Kuwait | |
Historically, most of present-day Kuwait was part of ancient Mesopotamia. Pre-oil Kuwait was a strategic trade port between Mesopotamia, Persia and India. Oil reserves were discovered in commercial quantities in 1938. In 1946, crude oil was exported for the first time. From 1946 to 1982, the country underwent large-scale modernization, largely based on income from oil production. In the 1980s, Kuwait experienced a period of geopolitical instability and an economic crisis following the stock market crash. In 1990, after oil production disputes with neighbouring Iraq, Kuwait was invaded, and later annexed into one of Iraq's governorates by Iraq under Saddam Hussein. The Iraqi occupation of Kuwait came to an end on February 26, 1991, after military intervention by a military coalition led by the United States and various other countries.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| KWD | Kuwaiti dinar | دك | 3 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| AR | Arabic language |
| EN | English language |