Kostroma Oblast (Kostroma Oblast)
 |
 |
Textile industries have been developed there since the early 18th century. Its major historic towns include Kostroma, Sharya, Nerekhta, Galich, Soligalich, and Makaryev.
From c. 300 CE the current area of Kostroma, with the exception of the area east of the Unzha River, was part of the Finno-Ugric peoples' lands, such as the Merya people and their loose tribal confederation. During the Neolithic era, comb-ceramics replaced prafinno-Ugric Volosovo. At the turn of 3rd and 2nd millennia BCE, the Fatyanovo culture arrived in the area, later to be assimilated into the tribes of the Late Bronze Age (the Abashevo culture and the Pozdnyakovskaya culture). The Finno-Ugric component as a result of migration and assimilation and grew even stronger since the culture of the early Iron Age. The people who developed the art of smelting of bog ore are already clearly Finno-Ugric in character. As a result of the mixing of the Finno-Ugric and pyanoborskoy Anan'ino local cultures with the Finno-Ugric Dyakovo culture came the Mari people, which began to take shape in Kostroma. Historically, the Kostroma region is a territory of Mari residence. In the currently existing settlements and the Old-Kazhirovo Shangskoe where the capitals of the Mari principalities of Yaksha and Sanga. Possession of these kingdoms in the north to reach the Great in earlier times. The village area was Odoevskoye SHARINSKY Mari fortress Bulaksy.
There were at least 109 Merya settlements located in the area of which the most important below mentioned trading centers and important hill fortresses were later recorded by the Russians as the Russians founded towns in the late 9th to 12th centuries.
With the death in 1277 of Basil Yaroslavovych, who had no children and left no heirs, the land principality as unclaimed moved into the Vladimir principality. Then, the Grand Duke Vladimir Alexandrovich Dmitry lost ground Kostroma principality to his brother Andrei Alexandrovich Gorodetsky, who in turn gave this inheritance to his nephew, the son of Dmitry Ivan Dmitrievich, but shortly after Ivan D. to possess Pereiaslavl-Zaleski and Kostroma principality newly departed Andrei Alexandrovich and then in 1299, he gave the land to his son Boris. After the latter's death in 1303, the prince of Kostroma in 1304 was the son of Daniel of Moscow, Boris Daniilovich. At this relative independence of the Principality of Kostroma ended and later it became part of the lands of the princely House of Moscow.
For the first time in what is now the area were separated from each other by Peter I: in 1708 by dividing the country into provinces were created in the province of Kostroma, Moscow province, and in the Galician province of Arkhangelsk province. In 1778, the two territories were re-united in the Kostroma governorship, which has been linked with the Yaroslavl first, then with the Nizhny Novgorod, and later with the Governor-General in one of Vladimir General Government.
In 1797 Paul I abolished the Governor-General Vladimir and Kostroma and Kostroma instead governorship was created Kostroma Province, which existed in constant borders until 1917.
The conversion of the Kostroma province center sped up its economic and cultural development, even though in 1773 and 1779, the city was completely burned in the fire fighting. Since 1781 the city began to be built on the master plan, which was based on a radial- concentric grid of streets that converged on a large semi-circular central area in the open side of the Volga.
The end of the 18th and the first half of the 19th century is rightly considered the rise in cultural development (architecture, painting, literature), not only of Kostroma but also of other county-level cities such as Galic, Nerekhta, and Soligalich. Architectural ensembles in the classical style still adorn the centers of these cities. There were widespread noble estates, which have become centers of culture in the remote outskirts of the province.
After the October Revolution of 1917, Kostroma Province became part formed in 1918 by the Russian Federation.
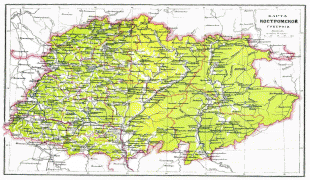
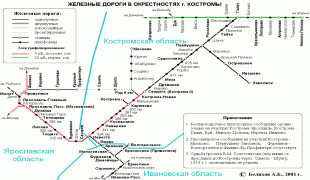
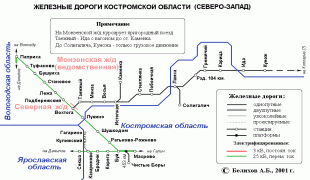
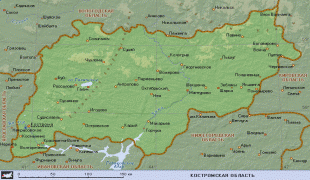
Map - Kostroma Oblast (Kostroma Oblast)
Map
Country - Russia
 |
 |
| Flag of Russia | |
The East Slavs emerged as a recognisable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries CE. The first East Slavic state, Kievan Rus', arose in the 9th century, and in 988, it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the Byzantine Empire. Rus' ultimately disintegrated, with the Grand Duchy of Moscow growing to become the Tsardom of Russia. By the early 18th century, Russia had vastly expanded through conquest, annexation, and the efforts of Russian explorers, developing into the Russian Empire, which remains the third-largest empire in history. However, with the Russian Revolution in 1917, Russia's monarchic rule was abolished and replaced by the Russian SFSR—the world's first constitutionally socialist state. Following the Russian Civil War, the Russian SFSR established the Soviet Union (with three other Soviet republics), within which it was the largest and principal constituent. At the expense of millions of lives, the Soviet Union underwent rapid industrialization in the 1930s, and later played a decisive role for the Allies of World War II by leading large-scale efforts on the Eastern Front. With the onset of the Cold War, it competed with the United States for global ideological influence; the Soviet era of the 20th century saw some of the most significant Russian technological achievements, including the first human-made satellite and the first human expedition into outer space.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| RUB | Russian ruble | ₽ | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| CE | Chechen language |
| CV | Chuvash language |
| KV | Komi language |
| RU | Russian language |
| TT | Tatar language |