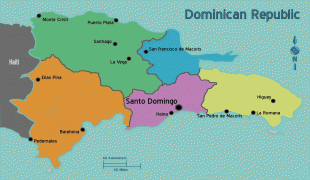
Dominican Republic (Dominican Republic)
 |
 |
| Flag of the Dominican Republic | |
The native Taíno people had inhabited Hispaniola before the arrival of Europeans, dividing it into five chiefdoms. They had constructed an advanced farming and hunting society, and were in the process of becoming an organized civilization. The Taínos also inhabited Cuba, Jamaica, Puerto Rico, and the Bahamas. The Genoese mariner Christopher Columbus explored and claimed the island for Castile, landing there on his first voyage in 1492. The colony of Santo Domingo became the site of the first permanent European settlement in the Americas and the first seat of Spanish colonial rule in the New World. It would also become the site to introduce importations of enslaved Africans to the Americas. In 1697, Spain recognized French dominion over the western third of the island, which became the independent state of Haiti in 1804.
After more than three hundred years of Spanish rule, the Dominican people declared independence in November 1821. The leader of the independence movement, José Núñez de Cáceres, intended the Dominican nation to unite with the country of Gran Colombia, but the newly independent Dominicans were forcefully annexed by Haiti in February 1822. Independence came 22 years later in 1844, after victory in the Dominican War of Independence. Over the next 72 years, the Dominican Republic experienced mostly civil wars (financed with loans from European merchants), several failed invasions by its neighbour, Haiti, and brief return to Spanish colonial status, before permanently ousting the Spanish during the Dominican War of Restoration of 1863–1865. During this period, three presidents were assassinated (José Antonio Salcedo in 1864, Ulises Heureaux in 1899, and Ramón Cáceres in 1911).
The U.S. occupied the Dominican Republic (1916–1924) due to threats of defaulting on foreign debts; a subsequent calm and prosperous six-year period under Horacio Vásquez followed. From 1930 the dictatorship of Rafael Leónidas Trujillo ruled until his assassination in 1961. Juan Bosch was elected president in 1962 but was deposed in a military coup in 1963. A civil war in 1965, the country's last, was ended by U.S. military intervention and was followed by the authoritarian rule of Joaquín Balaguer (1966–1978 and 1986–1996). Since 1978, the Dominican Republic has moved toward representative democracy, and has been led by Leonel Fernández for most of the time after 1996. Danilo Medina succeeded Fernández in 2012, winning 51% of the electoral vote over his opponent ex-president Hipólito Mejía. He was later succeeded by Luis Abinader in the 2020 presidential election after anti-government protests erupted that year.
The Dominican Republic has the largest economy (according to the U.S. State Department and the World Bank) in the Caribbean and Central American region and is the seventh-largest economy in Latin America. Over the last 25 years, the Dominican Republic has had the fastest-growing economy in the Western Hemisphere – with an average real GDP growth rate of 5.3% between 1992 and 2018. GDP growth in 2014 and 2015 reached 7.3 and 7.0%, respectively, the highest in the Western Hemisphere. In the first half of 2016, the Dominican economy grew 7.4% continuing its trend of rapid economic growth. Recent growth has been driven by construction, manufacturing, tourism, and mining. The country is the site of the third largest gold mine in the world, the Pueblo Viejo mine. Private consumption has been strong, as a result of low inflation (under 1% on average in 2015), job creation, and a high level of remittances. Income inequality, for generations an unsolved issue, has faded thanks to its rapid economic growth and now the Dominican Republic exhibits a Gini coefficient of 39, similar to that of Israel and Uruguay, and better than countries like the United States, Costa Rica or Chile. Illegal immigration from Haiti has resulted in government action. Immigration from Haiti has increased tensions between Dominicans and Haitians. The Dominican Republic is also home to 114,050 illegal immigrants from Venezuela. According to the UN, the country struggles with systemic racism and discrimination based on race, mostly targeted towards people of Haitian origin.
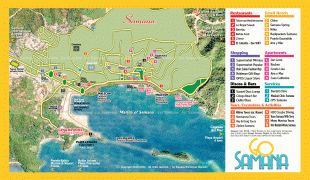
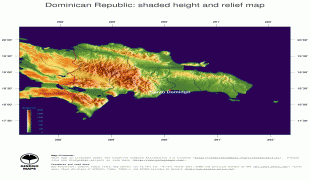
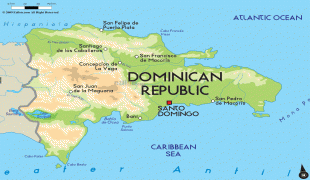
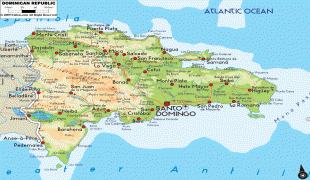
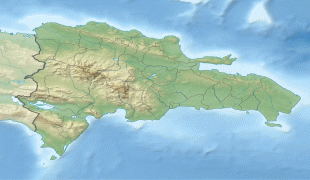
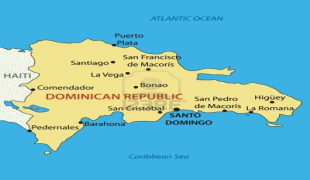
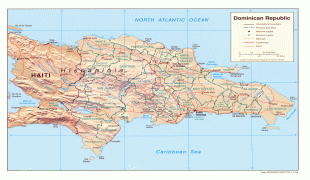
The Dominican Republic is the most visited destination in the Caribbean. The year-round golf courses and resorts are major attractions. A geographically diverse nation, the Dominican Republic is home to both the Caribbean's tallest mountain peak, Pico Duarte, and the Caribbean's largest lake and lowest point, Lake Enriquillo. The island has an average temperature of 26 °C and great climatic and biological diversity. The country is also the site of the first cathedral, castle, monastery, and fortress built in the Americas, located in Santo Domingo's Colonial Zone, a World Heritage Site. The Dominican Republic is highly vulnerable to natural disasters.
The name Dominican originates from Santo Domingo de Guzmán (Saint Dominic), the patron saint of astronomers, and founder of the Dominican Order.
The Dominican Order established a house of high studies on the colony of Santo Domingo that is now known as the Universidad Autónoma de Santo Domingo, the first University in the New World. They dedicated themselves to the education of the inhabitants of the island, and to the protection of the native Taíno people who were subjected to slavery.
For most of its history, up until independence, the colony was known simply as Santo Domingo – the name of its present capital and patron saint, Saint Dominic – and continued to be commonly known as such in English until the early 20th century. The residents were called "Dominicans" (Dominicanos), the adjectival form of "Domingo", and as such, the revolutionaries named their newly independent country the "Dominican Republic" (la República Dominicana).
In the national anthem of the Dominican Republic (himno nacional de la República Dominicana), the term "Dominicans" does not appear. The author of its lyrics, Emilio Prud'Homme, consistently uses the poetic term "Quisqueyans" (Quisqueyanos). The word "Quisqueya" derives from the Taíno language, and means "mother of the lands" (madre de las tierras). It is often used in songs as another name for the country. The name of the country in English is often shortened to "the D.R." (la R.D.), but this is rare in Spanish.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| DOP | Dominican peso | $ | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| ES | Spanish language |