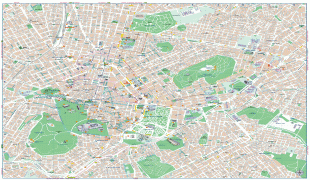
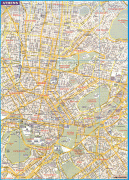
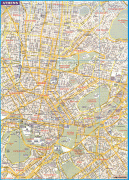
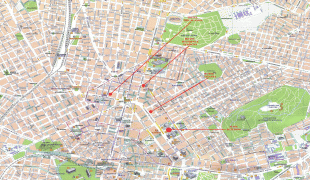
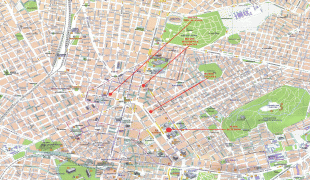
Athens
 |
 |
Classical Athens was a powerful city-state. It was a centre for the arts, learning and philosophy, and the home of Plato's Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum. It is widely referred to as the cradle of Western civilization and the birthplace of democracy, largely because of its cultural and political influence on the European continent—particularly Ancient Rome. In modern times, Athens is a large cosmopolitan metropolis and central to economic, financial, industrial, maritime, political and cultural life in Greece. In 2023, Athens' surrounding metropolitan area had a population of 3.1 million.
Athens is a Beta-status global city according to the Globalization and World Cities Research Network, and is one of the biggest economic centers in Southeastern Europe. It also has a large financial sector, and its port Piraeus is both the 5th largest passenger port in Europe, and the 24th largest in the world.
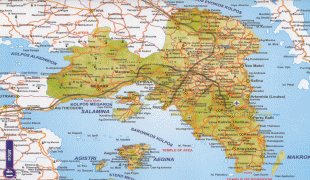
The Municipality of Athens (also City of Athens), which actually constitutes a small administrative unit of the entire urban area, had a population of 643,452 (in 2021) within its official limits, and a land area of 38.96 km2. The Athens Metropolitan Area or Greater Athens extends beyond its administrative municipal city limits, with a population of 3,744,059 (in 2021) over an area of 412 km2. Athens is also the southernmost capital on the European mainland and the warmest major city in continental Europe with an average annual temperature of up to 19.8 °C locally.
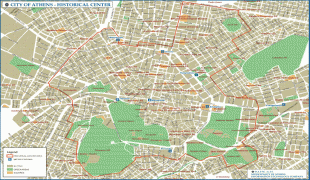
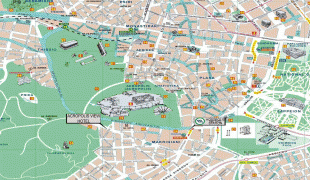
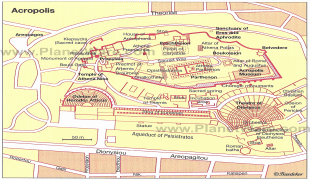
The heritage of the Classical Era is still evident in the city, represented by ancient monuments, and works of art, the most famous of all being the Parthenon, considered a key landmark of early Western civilization. The city also retains Roman, Byzantine and a smaller number of Ottoman monuments, while its historical urban core features elements of continuity through its millennia of history. Athens is home to two UNESCO World Heritage Sites, the Acropolis of Athens and the medieval Daphni Monastery. Landmarks of the modern era, dating back to the establishment of Athens as the capital of the independent Greek state in 1834, include the Hellenic Parliament and the so-called "Architectural Trilogy of Athens", consisting of the National Library of Greece, the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, and the Academy of Athens. Athens is also home to several museums and cultural institutions, such as the National Archeological Museum, featuring the world's largest collection of ancient Greek antiquities, the Acropolis Museum, the Museum of Cycladic Art, the Benaki Museum, and the Byzantine and Christian Museum. Athens was the host city of the first modern-day Olympic Games in 1896, and 108 years later it hosted the 2004 Summer Olympics, making it one of the few cities to have hosted the Olympics more than once. Athens joined the UNESCO Global Network of Learning Cities in 2016.
In Ancient Greek, the name of the city was Ἀθῆναι (Athênai, in Classical Attic) a plural. In earlier Greek, such as Homeric Greek, the name had been current in the singular form though, as Ἀθήνη (Athḗnē). It was possibly rendered in the plural later on, like those of Θῆβαι (Thêbai) and Μυκῆναι (Μukênai). The root of the word is probably not of Greek or Indo-European origin, and is possibly a remnant of the Pre-Greek substrate of Attica. In antiquity, it was debated whether Athens took its name from its patron goddess Athena (Attic Ἀθηνᾶ, Athēnâ, Ionic Ἀθήνη, Athḗnē, and Doric Ἀθάνα, Athā́nā) or Athena took her name from the city. Modern scholars now generally agree that the goddess takes her name from the city, because the ending -ene is common in names of locations, but rare for personal names.
According to the ancient Athenian founding myth, Athena, the goddess of wisdom and war, competed against Poseidon, the God of the Seas, for patronage of the yet-unnamed city; they agreed that whoever gave the Athenians the better gift would become their patron and appointed Cecrops, the king of Athens, as the judge. According to the account given by Pseudo-Apollodorus, Poseidon struck the ground with his trident and a salt water spring welled up. In an alternative version of the myth from Vergil's poem Georgics, Poseidon instead gave the Athenians the first horse. In both versions, Athena offered the Athenians the first domesticated olive tree. Cecrops accepted this gift and declared Athena the patron goddess of Athens. Eight different etymologies, now commonly rejected, have been proposed since the 17th century. Christian Lobeck proposed as the root of the name the word ἄθος (áthos) or ἄνθος (ánthos) meaning "flower", to denote Athens as the "flowering city". Ludwig von Döderlein proposed the stem of the verb θάω, stem θη- (tháō, thē-, "to suck") to denote Athens as having fertile soil. Athenians were called cicada-wearers (Τεττιγοφόροι) because they used to wear pins of golden cicadas. A symbol of being autochthonous (earth-born), because the legendary founder of Athens, Erechtheus was an autochthon or of being musicians, because the cicada is a "musician" insect. In classical literature, the city was sometimes referred to as the City of the Violet Crown, first documented in Pindar's ἰοστέφανοι Ἀθᾶναι (iostéphanoi Athânai), or as τὸ κλεινὸν ἄστυ (tò kleinòn ásty, "the glorious city").
During the medieval period, the name of the city was rendered once again in the singular as Ἀθήνα. Variant names included Setines, Satine, and Astines, all derivations involving false splitting of prepositional phrases. King Alphonse X of Castile gives the pseudo-etymology 'the one without death/ignorance'. In Ottoman Turkish, it was called Ātīnā, and in modern Turkish, it is Atina.
After the establishment of the modern Greek state, and partly due to the conservatism of the written language, Ἀθῆναι again became the official name of the city and remained so until the abandonment of Katharevousa in the 1970s, when Ἀθήνα, Athína, became the official name. Today, it is often simply called η πρωτεύουσα ī protévousa; 'the capital'.
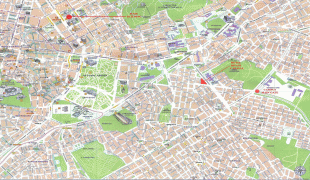
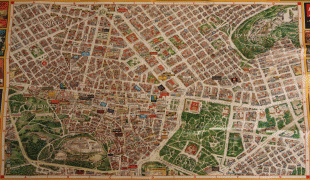
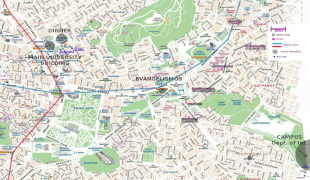
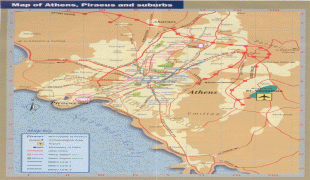
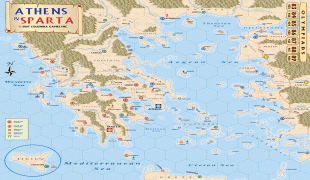
Map - Athens
Map
Country - Greece
 |
 |
| Flag of Greece | |
Greece is considered the cradle of Western civilization, being the birthplace of democracy, Western philosophy, Western literature, historiography, political science, major scientific and mathematical principles, theatre and the Olympic Games. From the eighth century BC, the Greeks were organised into various independent city-states, known as poleis (singular polis), which spanned the Mediterranean and the Black Sea. Philip II of Macedon united most of present-day Greece in the fourth century BC, with his son Alexander the Great rapidly conquering much of the ancient world, from the eastern Mediterranean to the North Western parts of India. The subsequent Hellenistic period saw the height of Greek culture and influence in antiquity. Greece was annexed by Rome in the second century BC, becoming an integral part of the Roman Empire and its continuation, the Byzantine Empire, which was culturally and linguistically predominantly Greek.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUR | Euro | € | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| EN | English language |
| FR | French language |
| EL | Greek language |