Flag of Dominica
The flag of Dominica was adopted on 3 November 1978, with some small changes having been made in 1981, 1988, and 1990. The original flag was designed by playwright Alwin Bully in early 1978 as the country prepared for independence.
It is one of only three national flags (the other two being El Salvador and Nicaragua) that currently use purple.
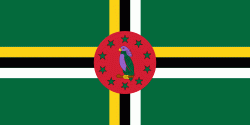
The flag, adopted in 1978, features the national bird emblem, the sisserou parrot (Amazona imperialis), which also appears on the coat of arms granted on 21 July 1961. This parrot, endemic to Dominica, is an endangered species with a population of only 250–350 individuals.
The green field represents the lush vegetation of the island. The cross represents the Trinity and Christianity, with its three colours symbolising the natives, the fertile soil, and the pure water. The 10 green five-pointed stars stand for the country's 10 parishes: (St Andrew, St David, St George, St John, St Joseph, St Luke, St Mark, St Patrick, St Paul, and St Peter), while the red disc stands for justice.
The sisserou parrot is sometimes coloured either blue or purple (the parrot's actual colour). The use of purple makes the flag of Dominica one of only three flags of sovereign states (alongside the flag of Nicaragua and the flag of El Salvador) to contain the colour.
The flag of Dominica, along with other national symbols, was the focus of a government-sponsored "Emblems Week" in 2016. An initiative of the independence committee, Emblems Week is aimed at reflecting on the meaning of the national emblems, and promoting their use among members of the general public and particularly among the country's schools.
It is one of only three national flags (the other two being El Salvador and Nicaragua) that currently use purple.
The flag, adopted in 1978, features the national bird emblem, the sisserou parrot (Amazona imperialis), which also appears on the coat of arms granted on 21 July 1961. This parrot, endemic to Dominica, is an endangered species with a population of only 250–350 individuals.
The green field represents the lush vegetation of the island. The cross represents the Trinity and Christianity, with its three colours symbolising the natives, the fertile soil, and the pure water. The 10 green five-pointed stars stand for the country's 10 parishes: (St Andrew, St David, St George, St John, St Joseph, St Luke, St Mark, St Patrick, St Paul, and St Peter), while the red disc stands for justice.
The sisserou parrot is sometimes coloured either blue or purple (the parrot's actual colour). The use of purple makes the flag of Dominica one of only three flags of sovereign states (alongside the flag of Nicaragua and the flag of El Salvador) to contain the colour.
The flag of Dominica, along with other national symbols, was the focus of a government-sponsored "Emblems Week" in 2016. An initiative of the independence committee, Emblems Week is aimed at reflecting on the meaning of the national emblems, and promoting their use among members of the general public and particularly among the country's schools.
National flag
Country - Dominica
Warning: getimagesize(/Image/Map/MP3575830.gif): failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/mapnlee7/public_html/MAPNALL/article.php on line 532
 |
 |
The island was settled by the Arawak arriving from South America in the fifth century. The Kalinago displaced the Arawak by the 15th century. Columbus is said to have passed the island on Sunday, 3 November 1493. It was later colonised by Europeans, predominantly by the French from the 1690s to 1763. The French imported enslaved people from West Africa to Dominica to work on coffee plantations. Great Britain took possession in 1763 after the Seven Years' War, and it gradually established English as its official language. The island gained independence as a republic in 1978.
