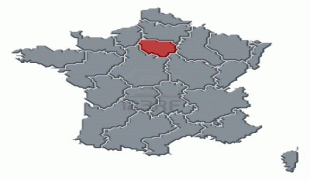
Île-de-France (Île-de-France)
 |
 |
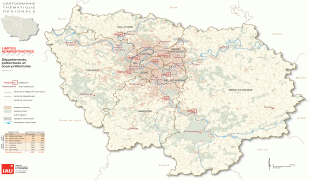
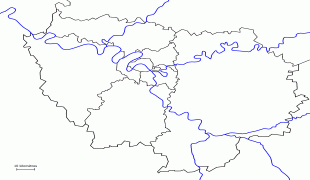
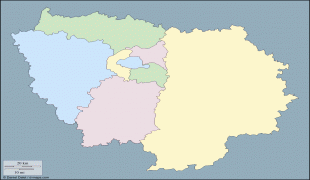
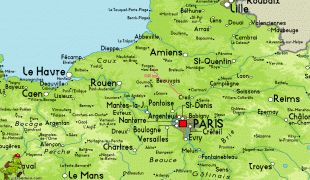
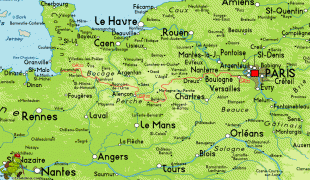
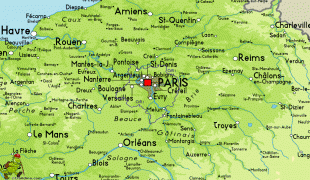
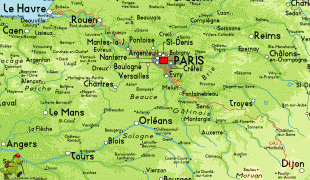
The region is made up of eight administrative departments: Paris, Essonne, Hauts-de-Seine, Seine-Saint-Denis, Seine-et-Marne, Val-de-Marne, Val-d'Oise and Yvelines. It was created as the "District of the Paris Region" in 1961. In 1976, when its status was aligned with the French administrative regions created in 1972, it was renamed after the historic province of Île-de-France. Residents are sometimes referred to as Franciliens, an administrative word created in the 1980s. The GDP of the region in 2019 was nearly one-third of the French, and 5% of the European Union's. It has the highest per capita GDP of any French region and the third highest of any region in the European Union.
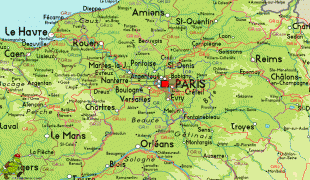
Beyond the city limits of Paris, the region has many other important historic sites, including the palaces of Versailles and Fontainebleau, as well as the most-visited tourist attraction in France, Disneyland Paris. Though it is the richest French region, a significant number of residents live in poverty: the official poverty rate in the Île-de-France was 15.9% in 2015. The region has witnessed increasing income inequality in recent decades and rising housing prices have pushed the less affluent outside Paris.
Although the modern name Île-de-France literally means "Island of France", its etymology is in fact unclear. The "island" may refer to the land between the rivers Oise, Marne and Seine, or it may also have been a reference to the Île de la Cité, where the French royal palace and cathedral were located.
Alternatively, the name may refer to the lands that were under the direct rule of the Capetian kings during the Middle Ages; thus, the lands were an "island" in a sea of various feudal territories ruled by vassals of the king.
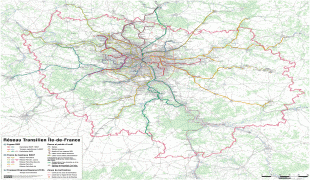
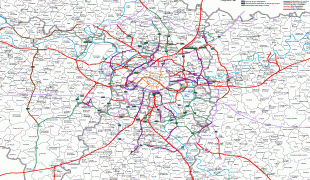
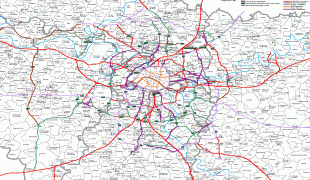
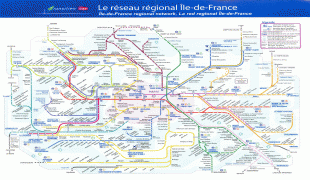
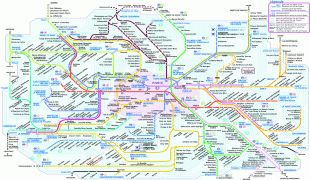
Map - Île-de-France (Île-de-France)
Map
Country - France
 |
 |
| Flag of France | |
Inhabited since the Palaeolithic era, the territory of Metropolitan France was settled by Celtic tribes known as Gauls during the Iron Age. Rome annexed the area in 51 BC, leading to a distinct Gallo-Roman culture that laid the foundation of the French language. The Germanic Franks formed the Kingdom of Francia, which became the heartland of the Carolingian Empire. The Treaty of Verdun of 843 partitioned the empire, with West Francia becoming the Kingdom of France in 987. In the High Middle Ages, France was a powerful but highly decentralised feudal kingdom. Philip II successfully strengthened royal power and defeated his rivals to double the size of the crown lands; by the end of his reign, France had emerged as the most powerful state in Europe. From the mid-14th to the mid-15th century, France was plunged into a series of dynastic conflicts involving England, collectively known as the Hundred Years' War, and a distinct French identity emerged as a result. The French Renaissance saw art and culture flourish, conflict with the House of Habsburg, and the establishment of a global colonial empire, which by the 20th century would become the second-largest in the world. The second half of the 16th century was dominated by religious civil wars between Catholics and Huguenots that severely weakened the country. France again emerged as Europe's dominant power in the 17th century under Louis XIV following the Thirty Years' War. Inadequate economic policies, inequitable taxes and frequent wars (notably a defeat in the Seven Years' War and costly involvement in the American War of Independence) left the kingdom in a precarious economic situation by the end of the 18th century. This precipitated the French Revolution of 1789, which overthrew the Ancien Régime and produced the Declaration of the Rights of Man, which expresses the nation's ideals to this day.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUR | Euro | € | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| EU | Basque language |
| BR | Breton language |
| CA | Catalan language |
| CO | Corsican language |
| FR | French language |
| OC | Occitan language |