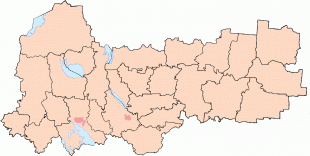
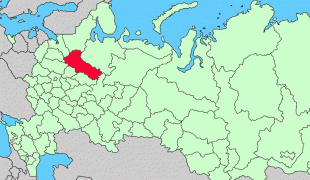
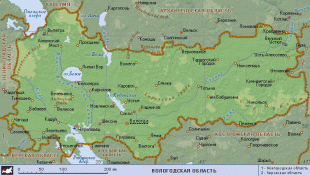
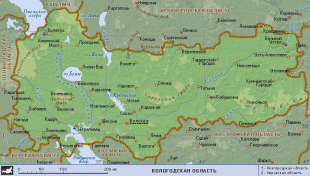
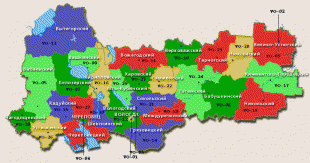
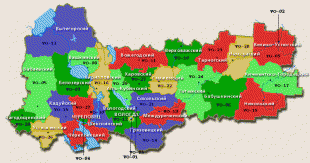
Vologda Oblast (Vologda Oblast)
 |
 |
Vologda Oblast is rich in historic monuments, such as the Kirillo-Belozersky Monastery, Ferapontov Monastery (a World Heritage Site) with the frescoes of Dionisius, medieval towns of Velikiy Ustyug and Belozersk, and baroque churches of Totma and Ustyuzhna.
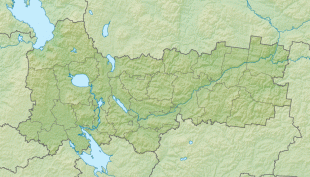
Large reserves of wood and fresh water are the main natural resources.
The area of Vologda Oblast was settled by Finnic peoples in prehistory, and most of the toponyms in the region are in fact Finnic. Vepsians, who still live in the west of the oblast, are the descendants of that population. Subsequently, the area was colonized by the Russians. Belozersk was mentioned in chronicles in 862 as one of the oldest towns in Russia. Much of the area was controlled by the Novgorod Republic, in particular, Totma was founded in 1152. Veliky Ustyug and the west of the current territory of the Oblast, with Belozersk and Ustyuzhna, belonged to the Vladimir-Suzdal Principality and were constantly threatened by Novgorod. Not later than in the 13th century the Novgorod merchants already reached the White Sea. They reached the area by using the waterways. The main waterway to the White Sea was the Northern Dvina, and Novgorod merchants used the Volga and its tributary, the Sheksna, along the Slavyanka River into Lake Nikolskoye, then the boats were taken by land to Lake Blagoveshchenskoye, from there downstream along the Porozovitsa River into Lake Kubenskoye and further to the Sukhona and the Northern Dvina.
In the 13th century, minor principalities started to proliferate. First, the Principality of Beloozero separated from Rostov, its northern and northeastern parts in the 15th century became quasi-independent, forming smaller feudal states like the Principality of Zaozerye or the Principality of Kubena. Many smaller principalities are only mentioned once in chronicles, and the very existence of these principalities is questionable. Between 1452 and 1481, Vologda was the center of the Principality of Vologda, the last independent principality in Vologda lands. By the end of the 15th century, all these lands were a part of the Great Duchy of Moscow.
In the 14th and the 15th centuries, the lands around Vologda became attractive for monks looking for desolate areas but still wishing to keep connections with the princes of Moscow. The princes, in their turn, viewed the monasteries as means to keep the influence of the Grand Duchy of Moscow in its remote areas. A number of influential monasteries, including Spaso-Prilutsky, Pavlo-Obnorsky, Kirillo-Belozersky, and Ferapontov monasteries, were founded. Kirillo-Belozersky Monastery soon became one of the most prominent Russian monasteries, with a lot of political influence, and successful economic development.
In the middle of the 15th century, the Vologda Lands were strongly involved with the Muscovite Civil War: Thus, Vasily the Blind was exiled to Vologda in 1446 and was released from his allegiance oath by the hegumen of the Kirillo-Belozersky Monastery, and by the late 1440s the Sukhona valley became the battlefield between the retreating army of Dmitry Shemyaka and the army of Vasily, chasing Shemyaka. During the Time of Troubles, the area was ravaged by Polish troops, who at some point besieged Vologda but did not succeed in conquering the city.
In the 17th century, Vologda was a prosperous city located on the main trading route from Moscow to Western Europe. During the reign of Tsar Peter the Great in the 18th century, Vologda became a shipbuilding center and played an important role in support of Russian military operations against Sweden. However, the importance of Vologda as a trade center was diminished after Saint Petersburg was founded in 1703, and the foreign trade was rerouted to the Baltic Sea. Peter even imposed restrictions on the White Sea trade.
Vologda was the northernmost territory where serfdom existed in Russia. In the lands west and south of Vologda, estates existed, but to the north and east of Vologda serfdom was never implemented, and the population owned their land.
In 1708, Peter the Great issued an edict which established seven governorates. The description of the borders of the governorates was not given; instead, their area was defined as a set of towns and the lands adjacent to those towns. Two of the governorates, Archangelgorod Governorate (east of the oblast) and Ingermanland Governorate (west of the oblast), were located in the present-day area of Vologda oblast. Vologda became a part of Archangelgorod Governorate. Subsequently, the western part of the Oblast was transferred to Novgorod Governorate. In 1780, Vologda became the administrative center of Vologda Viceroyalty which included the territory of the former Archangelgorod Governorate. Eventually, the viceroyalty was transformed into Vologda Governorate. After a sequence of further administrative reforms, Vologda Oblast was established in 1937.
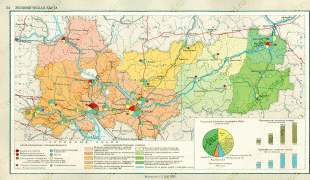
Map - Vologda Oblast (Vologda Oblast)
Map
Country - Russia
 |
 |
| Flag of Russia | |
The East Slavs emerged as a recognisable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries CE. The first East Slavic state, Kievan Rus', arose in the 9th century, and in 988, it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the Byzantine Empire. Rus' ultimately disintegrated, with the Grand Duchy of Moscow growing to become the Tsardom of Russia. By the early 18th century, Russia had vastly expanded through conquest, annexation, and the efforts of Russian explorers, developing into the Russian Empire, which remains the third-largest empire in history. However, with the Russian Revolution in 1917, Russia's monarchic rule was abolished and replaced by the Russian SFSR—the world's first constitutionally socialist state. Following the Russian Civil War, the Russian SFSR established the Soviet Union (with three other Soviet republics), within which it was the largest and principal constituent. At the expense of millions of lives, the Soviet Union underwent rapid industrialization in the 1930s, and later played a decisive role for the Allies of World War II by leading large-scale efforts on the Eastern Front. With the onset of the Cold War, it competed with the United States for global ideological influence; the Soviet era of the 20th century saw some of the most significant Russian technological achievements, including the first human-made satellite and the first human expedition into outer space.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| RUB | Russian ruble | ₽ | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| CE | Chechen language |
| CV | Chuvash language |
| KV | Komi language |
| RU | Russian language |
| TT | Tatar language |