New Caledonia (New Caledonia)
 |
 |
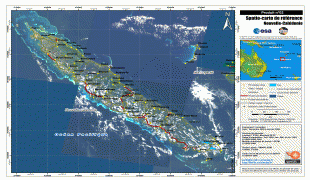
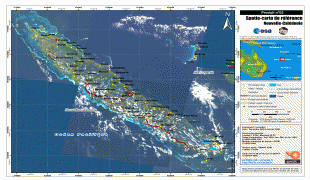
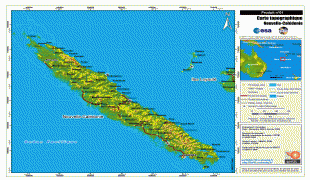
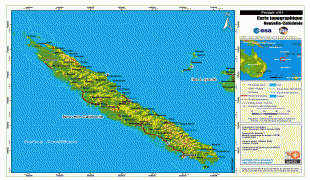
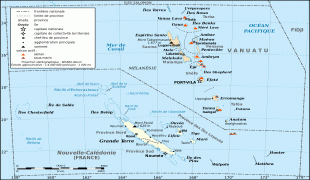
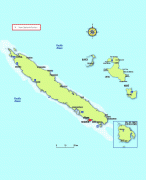
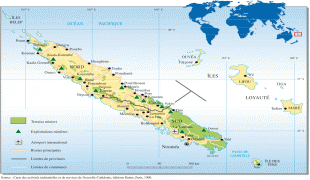
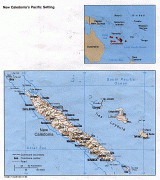
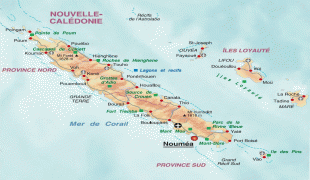
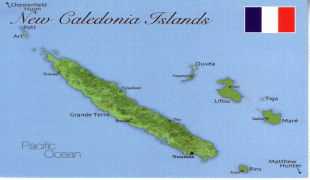
New Caledonia has a land area of 18576 km2 divided into three provinces. The North and South Provinces are on the New Caledonian mainland, while the Loyalty Islands Province is a series of three islands off the east coast of mainland. New Caledonia's population of 271,407 (October 2019 census) is of diverse origins and varies by geography; in the North and Loyalty Islands Provinces, the indigenous Kanak people predominate, while the wealthy South Province contains significant populations of European (Caldoches and Metropolitan French), Kanak, and Polynesian (mostly Wallisian) origin, as well as smaller groups of Southeast Asian, Pied-Noir, and North African heritage. The capital of New Caledonia is Nouméa.
New Caledonia was part of the continent Zealandia, which broke off from the supercontinent Gondwana between 79 million and 83 million years ago. The earliest traces of human presence in New Caledonia date back to the period when the Lapita culture was influential in large parts of the Pacific, c. 1600–500 BCE or 1300–200 BCE. The Lapita were highly skilled navigators and agriculturists. The first settlements were concentrated around the coast and date back to the period between c. 1100 BCE to 200 CE.
British explorer James Cook was the first European to sight New Caledonia, on 4 September 1774, during his second voyage. He named it "New Caledonia", as the northeast of the island reminded him of Scotland. The west coast of Grande Terre was approached by the Comte de Lapérouse in 1788, shortly before his disappearance, and the Loyalty Islands were first visited between 1793 and 1796 when Mare, Lifou, Tiga, and Ouvea were mapped by English whaler William Raven. Raven encountered the island, then named Britania, and today known as Maré (Loyalty Is.), in November 1793. From 1796 until 1840, only a few sporadic contacts with the archipelago were recorded. About 50 American whalers left record of being in the region (Grande Terre, Loyalty Is., Walpole and Hunter) between 1793 and 1887. Contacts with visiting ships became more frequent after 1840, because of their interest in sandalwood.
As trade in sandalwood declined, it was replaced by a new business enterprise, "blackbirding", a euphemism for taking Melanesian or Western Pacific Islanders from New Caledonia, the Loyalty Islands, New Hebrides, New Guinea, and the Solomon Islands into slavery, indentured or forced labour in the sugarcane plantations in Fiji and Queensland by various methods of trickery and deception. Blackbirding was practised by both French and Australian traders, but in New Caledonia's case, the trade in the early decades of the twentieth century involved kidnapping children from the Loyalty Islands to the Grand Terre for forced labour in plantation agriculture. New Caledonia's primary experience with blackbirding revolved around a trade from the New Hebrides (now Vanuatu) to the Grand Terre for labour in plantation agriculture, mines, as well as guards over convicts and in some public works. In the early years of the trade, coercion was used to lure Melanesian islanders onto ships. In later years indenture systems were developed; however, when it came to the French slave trade, which took place between its Melanesian colonies of the New Hebrides and New Caledonia, very few regulations were implemented. This represented a departure from contemporary developments in Australia, since increased regulations were developed to mitigate the abuses of blackbirding and 'recruitment' strategies on the coastlines.
The first missionaries from the London Missionary Society and the Marist Brothers arrived in the 1840s. In 1849, the crew of the American ship Cutter was killed and eaten by the Pouma clan. Cannibalism was widespread throughout New Caledonia.