Guangzhou
Guangzhou is at the heart of the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macau Greater Bay Area, the most-populous built-up metropolitan area in the world, which extends into the neighboring cities of Foshan, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen and part of Jiangmen, Huizhou, Zhuhai and Macau, forming the largest urban agglomeration on Earth with approximately 65,594,622 residents and part of the Pearl River Delta Economic Zone. Administratively, the city holds subprovincial status and is one of China's nine National Central Cities. In the late 1990s and early 2000s, nationals of sub-Saharan Africa who had initially settled in the Middle East and Southeast Asia moved in unprecedented numbers to Guangzhou in response to the 1997/98 Asian financial crisis. The domestic migrant population from other provinces of China in Guangzhou was 40% of the city's total population in 2008. Guangzhou has one of the most expensive real estate markets in China. As of the 2020 census, the registered population of the city's expansive administrative area was 18,676,605 individuals (up to 47% from the previous census in 2010) whom 16,492,590 lived in 9 urban districts (all but Conghua and Zengcheng). Guangzhou is the fifth most populous city by urban resident population in China after Shanghai, Beijing, Shenzhen and Chongqing.
In modern commerce, Guangzhou is best known for its annual Canton Fair, the oldest and largest trade fair in China. For three consecutive years (2013–2015), Forbes ranked Guangzhou as the best commercial city in mainland China. Guangzhou is highly ranked as an Alpha- (global first-tier) city together with San Francisco and Stockholm. It is a leading financial centre in the Asia-Pacific region and ranks 21st globally in the 2020 Global Financial Centres Index. As an important international city, Guangzhou has hosted numerous international and national sporting events, the most notable being the 2010 Asian Games, the 2010 Asian Para Games, and the 2019 FIBA Basketball World Cup. The city hosts 65 foreign representatives, making it the third major city to host more foreign representatives than any other city in China after Beijing and Shanghai. As of 2020, Guangzhou ranks 10th in the world and 5th in China (after Beijing, Shanghai, Hong Kong and Shenzhen) for the number of billionaire residents by the Hurun Global Rich List.
Guangzhou is a major centre of research and innovation in the Asia-Pacific with a high level of scientific research output, ranking 10th globally, 5th in the Asia-Pacific and 4th in China, and is home to many of China's most prestigious universities, including Sun Yat-sen University, South China University of Technology, Jinan University, South China Normal University, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou University, Southern Medical University, Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine.
Guǎngzhōu is the official romanization of the Chinese name. The name of the city is taken from the ancient "Guang Province" after it had become the prefecture's seat of government. The character or means "broad" or "expansive".
Before acquiring its current name, the town was known as Panyu (Punyü; ), a name still borne by one of Guangzhou's districts not far from the main city. The origin of the name is still uncertain, with 11 various explanations being offered, including that it may have referred to two local mountains. The city has also sometimes been known as Guangzhou Fu or Guangfu after its status as the capital of a prefecture. From this latter name, Guangzhou was known to medieval Persians such as Al-Masudi and Ibn Khordadbeh as Khanfu (خانفو). Under the Southern Han, the city was renamed Xingwang Fu.
The Chinese abbreviation for Guangzhou is "," pronounced Seoi6 in Cantonese and Suì in Mandarin (although the abbreviation on car license plates, as with the rest of the province, is ), after its nickname "City of Rice". The city has long borne the nickname City of Rams or City of the Five Rams from the five stones at the old Temple of the Five Immortals said to have been the sheep or goats ridden by the Taoist culture heroes credited with introducing rice cultivation to the area around the time of the city's foundation. The former name "City of the Immortals" (/五仙城) came from the same story. The more recent City of Flowers is usually taken as a simple reference to the area's fine greenery.
The English name "Canton" derived from Portuguese Cantão or Cidade de Cantão, a blend of dialectical pronunciations of "Guangdong" (e.g., Cantonese Gwong2-dung1). Although it originally and chiefly applied to the walled city, it was occasionally conflated with Guangdong by some authors. It was adopted as the Postal Map Romanization of Guangzhou, and remained the official name until its name change to "Guangzhou." As an adjective, it is still used in describing the people, language, cuisine and culture of Guangzhou and the surrounding Liangguang region. The 19th-century name was referred "Kwang-chow foo"
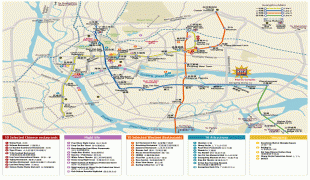
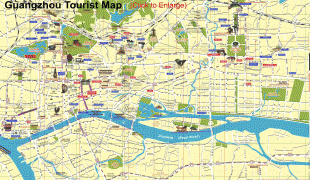
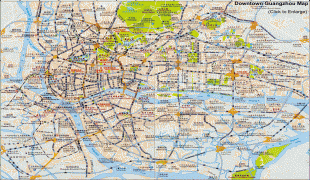
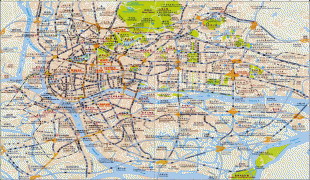
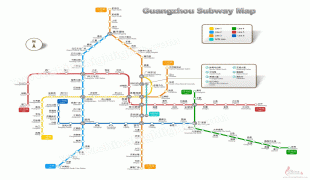
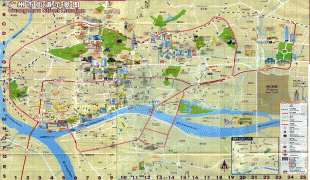
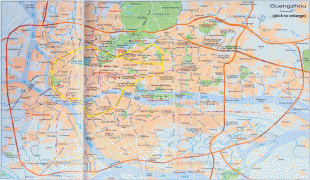
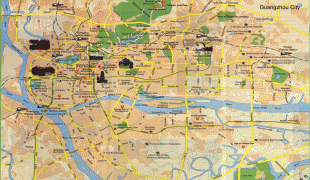
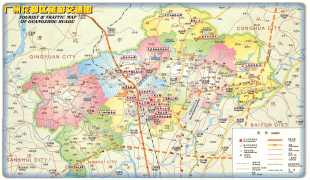
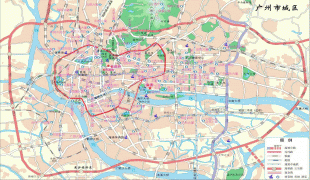
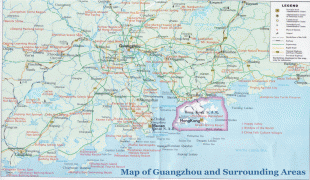
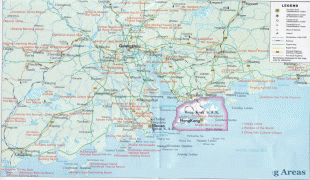
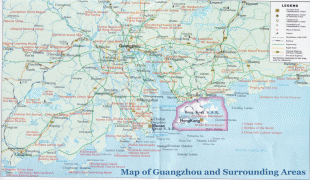
Map - Guangzhou
Map
Country - China
 |
 |
| Flag of China | |
Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dynasties. Chinese writing, Chinese classic literature, and the Hundred Schools of Thought emerged during this period and influenced China and its neighbors for centuries to come. In the third century BCE, Qin's wars of unification created the first Chinese empire, the short-lived Qin dynasty. The Qin was followed by the more stable Han dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE), which established a model for nearly two millennia in which the Chinese empire was one of the world's foremost economic powers. The empire expanded, fractured, and reunified; was conquered and reestablished; absorbed foreign religions and ideas; and made world-leading scientific advances, such as the Four Great Inventions: gunpowder, paper, the compass, and printing. After centuries of disunity following the fall of the Han, the Sui (581–618) and Tang (618–907) dynasties reunified the empire. The multi-ethnic Tang welcomed foreign trade and culture that came over the Silk Road and adapted Buddhism to Chinese needs. The early modern Song dynasty (960–1279) became increasingly urban and commercial. The civilian scholar-officials or literati used the examination system and the doctrines of Neo-Confucianism to replace the military aristocrats of earlier dynasties. The Mongol invasion established the Yuan dynasty in 1279, but the Ming dynasty (1368–1644) re-established Han Chinese control. The Manchu-led Qing dynasty nearly doubled the empire's territory and established a multi-ethnic state that was the basis of the modern Chinese nation, but suffered heavy losses to foreign imperialism in the 19th century.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNY | Renminbi | ¥ or 元 | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| ZH | Chinese language |
| UG | Uighur language |
| ZA | Zhuang language |