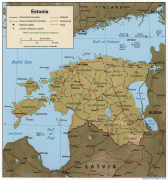
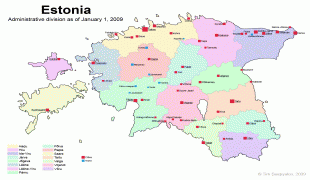
Estonia (Republic of Estonia)
 |
 |
| Flag of Estonia | |
The land of what is now modern Estonia has been inhabited by Homo sapiens since at least 9,000 BC. The medieval indigenous population of Estonia was one of the last pagan civilisations in Europe to adopt Christianity following the Papal-sanctioned Livonian Crusade in the 13th century. After centuries of successive rule by the Teutonic Order, Denmark, Sweden, and the Russian Empire, a distinct Estonian national identity began to emerge in the mid-19th century. This culminated in the 24 February 1918 Estonian Declaration of Independence from the then warring Russian and German Empires. Democratic throughout most of the interwar period, Estonia declared neutrality at the outbreak of World War II, but the country was repeatedly contested, invaded and occupied, first by the Soviet Union in 1940, then by Nazi Germany in 1941, and was ultimately reoccupied in 1944 by, and annexed into, the USSR as an administrative subunit (Estonian SSR). Throughout the 1944–1991 Soviet occupation, Estonia's de jure state continuity was preserved by diplomatic representatives and the government-in-exile. Following the bloodless Estonian "Singing Revolution" of 1988–1990, the nation's de facto independence from the Soviet Union was restored on 20 August 1991.
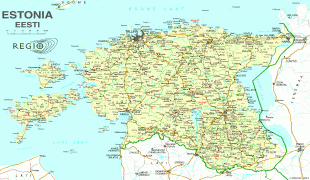
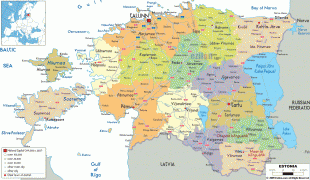
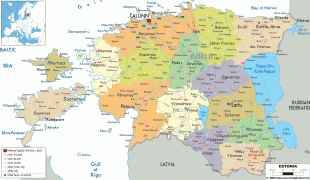
Estonia is a developed country, with an advanced high-income economy. The sovereign state of Estonia is a democratic unitary parliamentary republic, administratively subdivided into 15 maakond (counties). With a population of just over 1.3 million, it is one of the least populous members of the European Union, the Eurozone, the OECD, the Schengen Area, and NATO.
The name Estonia (Eesti ) has been connected to Aesti, a people first mentioned by Ancient Roman historian Tacitus around 98 AD. Some modern historians believe he was referring to Balts (i.e. not the Finnic-speaking ancestors of Estonians), while others have proposed that the name then applied to the whole eastern Baltic Sea region. Scandinavian sagas and Viking runestones referring to Eistland are the earliest known sources that definitely use the name in its modern geographic meaning. From Old Norse the toponym spread to other Germanic vernaculars and reached literary Latin by the end of 12th century when historian Saxo Grammaticus in his work Gesta Danorum referred to the area of what is now Estonia as Hestia or Estia, and its people as Estonum. The Livonian Chronicle of Henry (written ca. 1229) also used the name Estonia for the same area.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUR | Euro | € | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| ET | Estonian language |
| RU | Russian language |