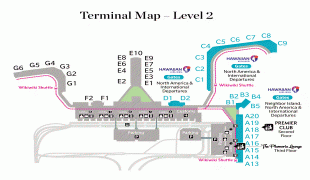
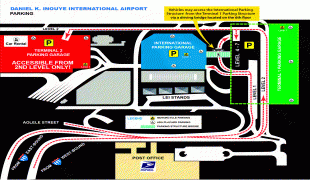
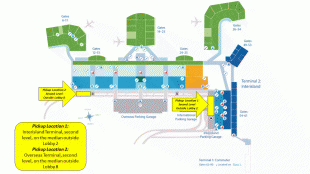
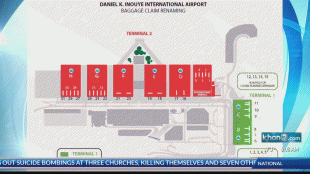
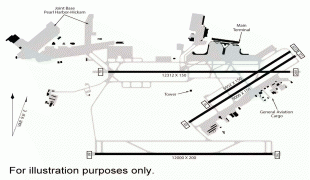
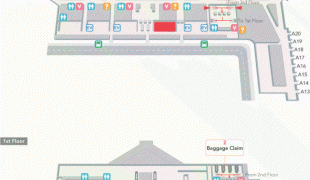
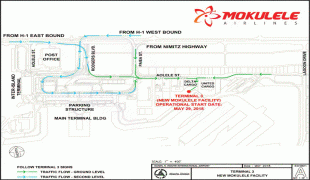
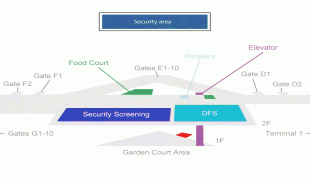
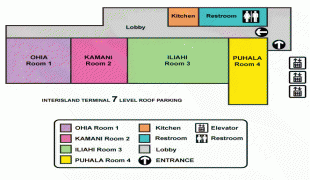
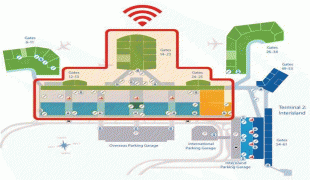
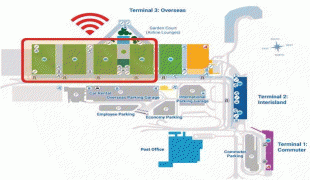
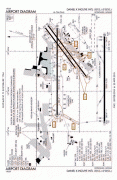
Daniel K. Inouye International Airport (Daniel K. Inouye International Airport)
Daniel K. Inouye International Airport, also known as Honolulu International Airport, is the main and largest airport in Hawaii. The airport is named after Honolulu native and Medal of Honor recipient Daniel Inouye, who represented Hawaii in the United States Senate from 1963 until his death in 2012. The airport is in the Honolulu census-designated place 3 miles (5 km) northwest of Honolulu's central business district. The airport covers 4,220 acres (1,708 ha), more than 1% of Oahu's land.
Daniel K. Inouye Airport offers nonstop flights to many places in North America, Asia, and Oceania. The airport serves as the main hub of Hawaiian Airlines and is also a base for Aloha Air Cargo. The airport is included in the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2017–2021, in which it is categorized as a large-hub primary commercial service facility.
The airport opened in March 1927 as John Rodgers Airport, after World War I naval officer John Rodgers. It was funded by the territorial legislature and the Chamber of Commerce, and was the first full airport in Hawaii; aircraft had previously been limited to small landing strips, fields, and seaplane docks. From 1939 to 1943, the adjacent Keehi Lagoon was dredged for use by seaplanes, and the dredged soil was moved to HNL to provide more space for conventional planes.
The U.S. military grounded all civil aircraft and took over all civil airports after the attack on Pearl Harbor, and Rodgers Field was designated Naval Air Station Honolulu. The Navy built a control tower and terminal building, and some commercial traffic was allowed during daylight hours. Rodgers Field was returned to the Territory of Hawaii in 1946. At the time, at 4019 acre, it was one of the largest airports in the United States, with four paved land runways and three seaplane runways.
John Rodgers Airport was renamed Honolulu Airport in 1947; "International" being added to the name in 1951. Being near the center of the Pacific Ocean it was a stop for many transpacific flights. By 1950, it was the third-busiest airport in the United States in terms of aircraft operations, and its 13097 ft runway was the world's longest in 1953. In summer 1959, Qantas began the first jet service to Honolulu on its flights between Australia and California. Qantas introduced these jet flights with Boeing 707 aircraft operating a routing of Sydney – Fiji – Honolulu – San Francisco. Aeronautical engineer and airline consultant Frank Der Yuen advised in the design of the original building and founded its aerospace museum.
The original terminal building on the southeast side of runways 4 was replaced by the John Rodgers Terminal, which was dedicated on August 22, 1962, and opened on October 14, 1962. From 1970 through 1978, the architect Vladimir Ossipoff designed a terminal modernization project that remodeled this terminal and created several additions, which included the Diamond Head Concourse in 1970, the Ewa Concourse in 1972, and the Central Concourse in 1980.
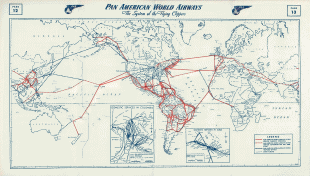
Pan American World Airways (Pan Am) used Honolulu as a transpacific hub for many years, initially as a connecting point between the West Coast and Polynesia (Fiji, New Caledonia, and New Zealand) in 1946, followed by service to East Asia through Midway Island and Wake Island from 1947. By 1960, Pan American was serving the airport with Boeing 707 jets. Pan Am flight number 1, operating a 707, flew a westbound routing of San Francisco – Honolulu – Wake Island – Tokyo – Hong Kong and continuing on to New York City via stops in Asia and Europe. The airline also operated nonstop 707 service to Portland, Oregon (continuing to Seattle) and Los Angeles. Pan Am also had direct 707 flights from Honolulu to Calcutta, Guam, Jakarta, Karachi, Manila, Rangoon, Saigon, and Singapore in 1960. United Airlines was flying nonstop Douglas DC-6 "Mainliner" service from San Francisco in 1947 and by 1961 was operating Douglas DC-8 jet service nonstop from Los Angeles and San Francisco with direct one-stop DC-8 flights from both Chicago and New York City. British Commonwealth Pacific Airlines (BCPA) began serving the airport during the mid-1940s with Douglas DC-4 aircraft flying a routing of Sydney – Auckland – Fiji – Canton Island – Honolulu – San Francisco – Vancouver, B.C. In 1950, Northwest Airlines was operating nonstop flights from Seattle with Boeing 377 Stratocruiser propliners; by 1961, Northwest was flying daily Douglas DC-8 jet service on a round trip routing of New York City – Chicago – Seattle – Portland, OR – Honolulu. Also in 1950, Canadian Pacific Air Lines (which later became CP Air) was operating service between western Canada and Australia with a routing of Vancouver – Honolulu – Canton Island – Fiji – Sydney.
Honolulu-based air carriers Aloha Airlines and Hawaiian Airlines had both introduced jet service on their respective inter-island routes in Hawaii by 1966 with Aloha operating British Aircraft Corporation BAC One-Eleven jets and Hawaiian flying Douglas DC-9-10 jets with both airlines also continuing to operate turboprops on their island services at this time. According to their respective timetables, Aloha was flying Fairchild F-27 and Vickers Viscount propjets while Hawaiian was operating Convair 640 propjets in addition to their new jet aircraft in 1966. Both local air carriers would eventually operate service to the U.S. mainland as well as to the South Pacific while continuing to operate inter-island flights. In 1986, Hawaiian was operating nonstop Lockheed L-1011 Tristar service from Honolulu to Las Vegas, Los Angeles, San Francisco, and Seattle as well as one-stop direct service to Portland, Oregon, and also nonstop Douglas DC-8 service to Pago Pago with this flight continuing on to Tonga. By 2003, Aloha was flying nonstop Boeing 737-700 service to Burbank, Oakland, Orange County, and Vancouver, B.C., with one-stop service to Las Vegas, Phoenix, Reno, and Sacramento in addition to operating nonstop flights to Kwajalein and Pago Pago with one-stop service to Majuro and Rarotonga.
In the spring of 1969, Braniff International introduced nonstop Boeing 707-320 service to Honolulu from Dallas Love Field, Houston Hobby Airport, and St. Louis, with one-stop service from Atlanta, Miami, and New Orleans. At the same time, United Airlines introduced daily nonstop Douglas DC-8-62 flights from New York City and was continuing to operate nonstop DC-8 service to Honolulu from Los Angeles and San Francisco. Also in 1969, Western Airlines was operating nonstop Boeing 707 and Boeing 720B service not only from several California cities but also from Anchorage, Denver, Minneapolis–St. Paul, and Phoenix. By 1981, Western was operating one-stop McDonnell Douglas DC-10-30 service from London Gatwick Airport via a polar route with a stop in Anchorage. By the mid-1970s Pan Am offered nonstop service from Honolulu to Japan, Guam, Australia, New Zealand, and Fiji, as well as to cities on the West Coast. Continental Airlines used Honolulu as a stopover point for charter service to Southeast Asia during the Vietnam War era, and to feed its Guam-based Air Micronesia operation. By the early 1970s, Continental was operating scheduled nonstop flights between Honolulu and Los Angeles, Portland, Oregon, and Seattle, including Boeing 747-100 nonstops from Los Angeles and one-stop 747 flights from Chicago. Air Micronesia had service to Guam via stops at Midway Island, Kwajalein, Majuro, Ponape, (now Pohnpei) and Truk (now Chuuk State) flying a Boeing 727-100. American Airlines also operated flights to Auckland, Sydney, Fiji and Pago Pago via Honolulu during the early 1970s in addition to operating nonstop Boeing 707-320 flights from St. Louis.
Over the years, many foreign air carriers used Honolulu as a transpacific stopover point, including Air New Zealand, BOAC (now British Airways), British Commonwealth Pacific Airlines, Canadian Pacific Air Lines, China Airlines, Garuda Indonesia, Japan Airlines, Korean Air, Philippine Airlines, Qantas, Real Transportes Aereos (a Brazilian airline), and Singapore Airlines as well as French air carriers Union de Transports Aeriens (UTA) and its predecessor Transports Aeriens Intercontinentaux (TAI). BOAC served Honolulu as part of its around the world services during the 1960s and early 1970s, first with Bristol Britannia turboprop airliners and later with Boeing 707 and Vickers VC10 jets. Pan Am and Trans World Airlines (TWA) also served Honolulu as a stop on their respective around the world services during the early 1970s. In 1979, Braniff International was operating all of its flights from the airport with Boeing 747 aircraft with nonstops to Dallas–Fort Worth, Guam, and Los Angeles as well as one-stop service to Hong Kong and also one-stop service to Bogota in South America. Several small airlines based in the South Pacific also served Honolulu. In 1983, Air Nauru was operating Boeing 737-200 nonstop flights from Majuro with direct service from Nauru, Air Niugini was flying Boeing 707 aircraft nonstop from Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea and Air Tungaru was operating Boeing 727-100 aircraft nonstop from Christmas Island. Also in 1983, Honolulu-based South Pacific Island Airways was operating nonstop Boeing 707 service from Anchorage, Guam, Pago Pago and Papeete.
Daniel K. Inouye Airport offers nonstop flights to many places in North America, Asia, and Oceania. The airport serves as the main hub of Hawaiian Airlines and is also a base for Aloha Air Cargo. The airport is included in the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2017–2021, in which it is categorized as a large-hub primary commercial service facility.
The airport opened in March 1927 as John Rodgers Airport, after World War I naval officer John Rodgers. It was funded by the territorial legislature and the Chamber of Commerce, and was the first full airport in Hawaii; aircraft had previously been limited to small landing strips, fields, and seaplane docks. From 1939 to 1943, the adjacent Keehi Lagoon was dredged for use by seaplanes, and the dredged soil was moved to HNL to provide more space for conventional planes.
The U.S. military grounded all civil aircraft and took over all civil airports after the attack on Pearl Harbor, and Rodgers Field was designated Naval Air Station Honolulu. The Navy built a control tower and terminal building, and some commercial traffic was allowed during daylight hours. Rodgers Field was returned to the Territory of Hawaii in 1946. At the time, at 4019 acre, it was one of the largest airports in the United States, with four paved land runways and three seaplane runways.
John Rodgers Airport was renamed Honolulu Airport in 1947; "International" being added to the name in 1951. Being near the center of the Pacific Ocean it was a stop for many transpacific flights. By 1950, it was the third-busiest airport in the United States in terms of aircraft operations, and its 13097 ft runway was the world's longest in 1953. In summer 1959, Qantas began the first jet service to Honolulu on its flights between Australia and California. Qantas introduced these jet flights with Boeing 707 aircraft operating a routing of Sydney – Fiji – Honolulu – San Francisco. Aeronautical engineer and airline consultant Frank Der Yuen advised in the design of the original building and founded its aerospace museum.
The original terminal building on the southeast side of runways 4 was replaced by the John Rodgers Terminal, which was dedicated on August 22, 1962, and opened on October 14, 1962. From 1970 through 1978, the architect Vladimir Ossipoff designed a terminal modernization project that remodeled this terminal and created several additions, which included the Diamond Head Concourse in 1970, the Ewa Concourse in 1972, and the Central Concourse in 1980.
Pan American World Airways (Pan Am) used Honolulu as a transpacific hub for many years, initially as a connecting point between the West Coast and Polynesia (Fiji, New Caledonia, and New Zealand) in 1946, followed by service to East Asia through Midway Island and Wake Island from 1947. By 1960, Pan American was serving the airport with Boeing 707 jets. Pan Am flight number 1, operating a 707, flew a westbound routing of San Francisco – Honolulu – Wake Island – Tokyo – Hong Kong and continuing on to New York City via stops in Asia and Europe. The airline also operated nonstop 707 service to Portland, Oregon (continuing to Seattle) and Los Angeles. Pan Am also had direct 707 flights from Honolulu to Calcutta, Guam, Jakarta, Karachi, Manila, Rangoon, Saigon, and Singapore in 1960. United Airlines was flying nonstop Douglas DC-6 "Mainliner" service from San Francisco in 1947 and by 1961 was operating Douglas DC-8 jet service nonstop from Los Angeles and San Francisco with direct one-stop DC-8 flights from both Chicago and New York City. British Commonwealth Pacific Airlines (BCPA) began serving the airport during the mid-1940s with Douglas DC-4 aircraft flying a routing of Sydney – Auckland – Fiji – Canton Island – Honolulu – San Francisco – Vancouver, B.C. In 1950, Northwest Airlines was operating nonstop flights from Seattle with Boeing 377 Stratocruiser propliners; by 1961, Northwest was flying daily Douglas DC-8 jet service on a round trip routing of New York City – Chicago – Seattle – Portland, OR – Honolulu. Also in 1950, Canadian Pacific Air Lines (which later became CP Air) was operating service between western Canada and Australia with a routing of Vancouver – Honolulu – Canton Island – Fiji – Sydney.
Honolulu-based air carriers Aloha Airlines and Hawaiian Airlines had both introduced jet service on their respective inter-island routes in Hawaii by 1966 with Aloha operating British Aircraft Corporation BAC One-Eleven jets and Hawaiian flying Douglas DC-9-10 jets with both airlines also continuing to operate turboprops on their island services at this time. According to their respective timetables, Aloha was flying Fairchild F-27 and Vickers Viscount propjets while Hawaiian was operating Convair 640 propjets in addition to their new jet aircraft in 1966. Both local air carriers would eventually operate service to the U.S. mainland as well as to the South Pacific while continuing to operate inter-island flights. In 1986, Hawaiian was operating nonstop Lockheed L-1011 Tristar service from Honolulu to Las Vegas, Los Angeles, San Francisco, and Seattle as well as one-stop direct service to Portland, Oregon, and also nonstop Douglas DC-8 service to Pago Pago with this flight continuing on to Tonga. By 2003, Aloha was flying nonstop Boeing 737-700 service to Burbank, Oakland, Orange County, and Vancouver, B.C., with one-stop service to Las Vegas, Phoenix, Reno, and Sacramento in addition to operating nonstop flights to Kwajalein and Pago Pago with one-stop service to Majuro and Rarotonga.
In the spring of 1969, Braniff International introduced nonstop Boeing 707-320 service to Honolulu from Dallas Love Field, Houston Hobby Airport, and St. Louis, with one-stop service from Atlanta, Miami, and New Orleans. At the same time, United Airlines introduced daily nonstop Douglas DC-8-62 flights from New York City and was continuing to operate nonstop DC-8 service to Honolulu from Los Angeles and San Francisco. Also in 1969, Western Airlines was operating nonstop Boeing 707 and Boeing 720B service not only from several California cities but also from Anchorage, Denver, Minneapolis–St. Paul, and Phoenix. By 1981, Western was operating one-stop McDonnell Douglas DC-10-30 service from London Gatwick Airport via a polar route with a stop in Anchorage. By the mid-1970s Pan Am offered nonstop service from Honolulu to Japan, Guam, Australia, New Zealand, and Fiji, as well as to cities on the West Coast. Continental Airlines used Honolulu as a stopover point for charter service to Southeast Asia during the Vietnam War era, and to feed its Guam-based Air Micronesia operation. By the early 1970s, Continental was operating scheduled nonstop flights between Honolulu and Los Angeles, Portland, Oregon, and Seattle, including Boeing 747-100 nonstops from Los Angeles and one-stop 747 flights from Chicago. Air Micronesia had service to Guam via stops at Midway Island, Kwajalein, Majuro, Ponape, (now Pohnpei) and Truk (now Chuuk State) flying a Boeing 727-100. American Airlines also operated flights to Auckland, Sydney, Fiji and Pago Pago via Honolulu during the early 1970s in addition to operating nonstop Boeing 707-320 flights from St. Louis.
Over the years, many foreign air carriers used Honolulu as a transpacific stopover point, including Air New Zealand, BOAC (now British Airways), British Commonwealth Pacific Airlines, Canadian Pacific Air Lines, China Airlines, Garuda Indonesia, Japan Airlines, Korean Air, Philippine Airlines, Qantas, Real Transportes Aereos (a Brazilian airline), and Singapore Airlines as well as French air carriers Union de Transports Aeriens (UTA) and its predecessor Transports Aeriens Intercontinentaux (TAI). BOAC served Honolulu as part of its around the world services during the 1960s and early 1970s, first with Bristol Britannia turboprop airliners and later with Boeing 707 and Vickers VC10 jets. Pan Am and Trans World Airlines (TWA) also served Honolulu as a stop on their respective around the world services during the early 1970s. In 1979, Braniff International was operating all of its flights from the airport with Boeing 747 aircraft with nonstops to Dallas–Fort Worth, Guam, and Los Angeles as well as one-stop service to Hong Kong and also one-stop service to Bogota in South America. Several small airlines based in the South Pacific also served Honolulu. In 1983, Air Nauru was operating Boeing 737-200 nonstop flights from Majuro with direct service from Nauru, Air Niugini was flying Boeing 707 aircraft nonstop from Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea and Air Tungaru was operating Boeing 727-100 aircraft nonstop from Christmas Island. Also in 1983, Honolulu-based South Pacific Island Airways was operating nonstop Boeing 707 service from Anchorage, Guam, Pago Pago and Papeete.
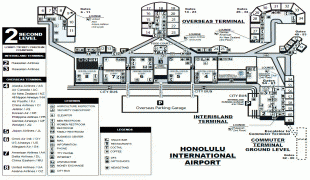
Map - Daniel K. Inouye International Airport (Daniel K. Inouye International Airport)
Country - United_States
 |
 |
| Flag of the United States | |
Indigenous peoples have inhabited the Americas for thousands of years. Beginning in 1607, British colonization led to the establishment of the Thirteen Colonies in what is now the Eastern United States. They quarreled with the British Crown over taxation and political representation, leading to the American Revolution and proceeding Revolutionary War. The United States declared independence on July 4, 1776, becoming the first nation-state founded on Enlightenment principles of unalienable natural rights, consent of the governed, and liberal democracy. The country began expanding across North America, spanning the continent by 1848. Sectional division surrounding slavery in the Southern United States led to the secession of the Confederate States of America, which fought the remaining states of the Union during the American Civil War (1861–1865). With the Union's victory and preservation, slavery was abolished nationally by the Thirteenth Amendment.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| USD | United States dollar | $ | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| EN | English language |
| FR | French language |
| ES | Spanish language |